Bcs Class Iv 5,0/5 5401 reviews
Feb 28, 2017 - BCS class IV drugs (e.g., amphotericin B, furosemide, acetazolamide, ritonavir, paclitaxel) exhibit many characteristics that are problematic for. FDA has issued a final guidance entitled Waiver of In-vivo Bioavailability and Bioequivalence Studies for Immediate Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms Based on a Biopharmaceutics Classification System. Oct 3, 2018 - Bulletin. Bio Pharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) Class IV Drug. Nanoparticles: Quantum Leap to Improve Their Therapeutic Index.
- Bcs Class Iv Drugs List
- Bcs Class Iv Drugs List
- Bcs Classification System
Bioavailability enhancement techniques for BCS Class II and Class IV drugs 3 rd International Conference and Exhibition on Biowaivers, Biologics & Biosimilars Jithan Venkata Aukunuru Keynote: DOI: Abstract Bioavailability is the rate and extent (amount) of absorption of unchanged drug from its dosage form. It is one of the important parameter to achieve desired concentration of drug in systemic circulation for pharmacological response to be shown. A drug with poor bioavailability is one with poor aqueous solubility, slow dissolution rate in biological fluids, poor stability of dissolved drug at physiological pH, poor permeation through biomembrane, extensive presystemic metabol ism. From BCS candidates, class II and class IV drugs have solubility and permeability problems because of which their bioavailability is poor.
Poorly water soluble drugs often require high doses in order to reach therapeutic plasma concentrations after oral administration. Low aqueous solubility is the major problem encountered with formulation development of new chemical entities.
Any drug to be absorbed must be present in the form of an aqueous solution at the site of absorption. This presentation focuses on the various techniques used for the improvement of the Bioavailability of BCS class II and class IV drugs including size reduction, solubilising excipients, colloidal drug delivery systems, pH adjustment, solid dispersion, complexation, cosolvency, micellar solubilisation, hydrotropy etc.
Biography Jithan Venkata Aukunuru is presently a Professor and Principal at Mother Teresa College of Pharmacy (Affiliated to Osmania University), Hyderabad. Jithan is a recipient of several awards and medals in his entire academic career. His research interests include Novel Oral Delivery Technologies; Exploratory Pharmaceutics; IVIVC; Implants; Nanosuspensions; Microspheres; Proliposomes; Prodrugs; Colon Drug Delivery; Nanotechnology; Chronotherapeutics; Novel Transdermal Delivery Methods; Exploratory Pharmaceutics; Drug Metabolism; Pharmacology (Retinal and Liver Disorders); Solubility Enhancement. He was awarded Ph.D in 2002 from University of Nebraska Medical Sciences, USA, in Pharmaceutical Sciences. For his PhD, he worked on retinal delivery of small and macromolecules. He is a fellow of Association for Biotechnology & Pharmacy and an active member of APP, APTI, IPA and IPGA. .
Bcs Class Iv Drugs List

Bcs Class Iv Drugs List
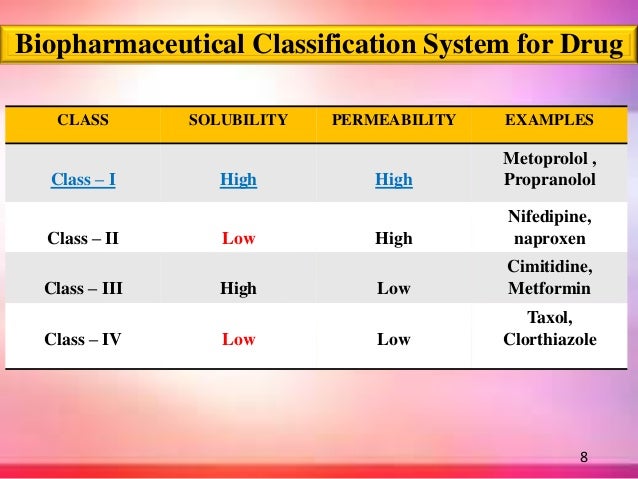
Contents • • • • • • BCS classes [ ] According to the Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS) drug substances are classified to four classes upon their solubility and permeability: • Class I - high, high • Example: • Those compounds are well absorbed and their absorption rate is usually higher than excretion. • Class II - high permeability, low solubility • Example:,,, paracetamol, • The of those products is limited by their solvation rate. A correlation between the bioavailability and the solvation can be found. • Class III - low permeability, high solubility • Example: • The absorption is limited by the permeation rate but the drug is solvated very fast. If the formulation does not change the permeability or gastro-intestinal duration time, then class I criteria can be applied. • Class IV - low permeability, low solubility • Example: • Those compounds have a poor bioavailability.
Mr photo download windows 10. Some PCs may require a 4K capable monitor (sold separately).
Pengenalan kepada perniagaan. Usually they are not well absorbed over the intestinal mucosa and a high variability is expected. Definitions [ ] The drugs are classified in BCS on the basis of solubility, permeability, and dissolution. Solubility class boundaries are based on the highest dose strength of an immediate release product.
Bcs Classification System
A drug is considered highly soluble when the highest dose strength is soluble in 250 ml or less of aqueous media over the pH range of 1 to 7.5. The volume estimate of 250 ml is derived from typical bioequivalence study protocols that prescribe administration of a drug product to fasting human volunteers with a glass of water. Driver finder pro 3.7.1 crack. Permeability class boundaries are based indirectly on the extent of absorption of a drug substance in humans and directly on the measurement of rates of mass transfer across human intestinal membrane. Alternatively non-human systems capable of predicting drug absorption in humans can be used (such as in-vitro culture methods).

